Micro-FTIR & Rapt-IR
General Information
In 2019, the European Chemical Agency clearly defined microplastics and their sizes: “a material composed of solid polymer-containing particles, to which additives or other substances may have been added, with particle dimensions ranging from 1 nm to 5 mm and with fiber lengths ranging from 3 nm to 15 mm and a length-to-diameter ratio of >3. ECHA has also firmly stated that polymer identification during microplastics analysis is fundamental. Plastic additives can have different interactions with polymers, being added at any stage during the production of plastic objects. Some of them are embedded with polymers, such as cross-linkers or plasticizers, while others are loosely bound to the plastic objects, e.g., finishing agents for textiles or extruding agents. Particles Analysis provides an accurate simultaneous quantification (via microscopic counting) and characterization (unequivocal identification) of microplastics and other anthropogenic particles, by also employing various reference libraries. This allows for evaluating the environmental risk assessment and designing future actions of environmental management and recovery. Identification and quantification are performed simultaneously. Thanks to the non-destructive pretreatment methods developed, the minimum size analyzed (LOD) is 5 µm.
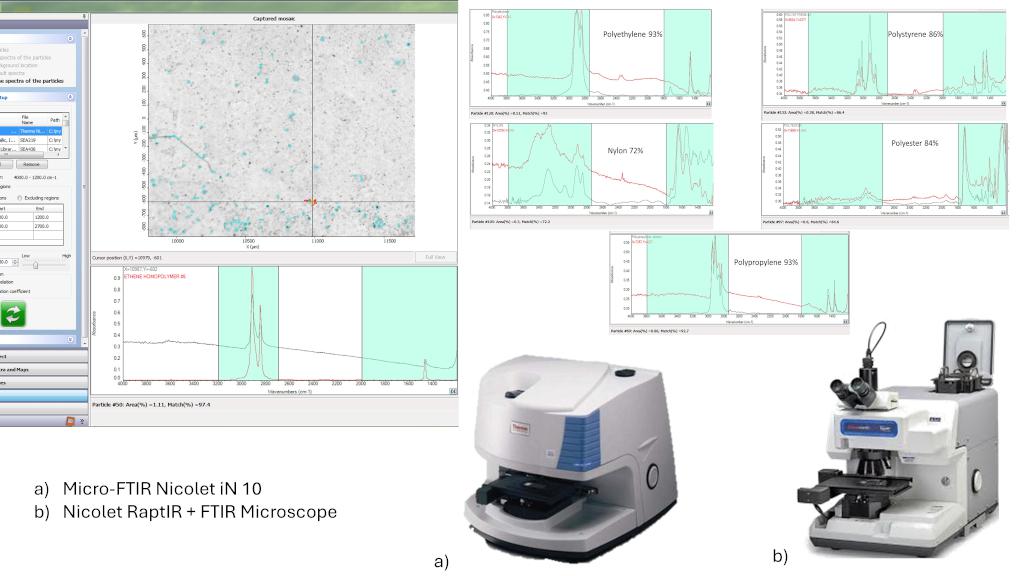
Technical description
Micro-FTIR Nicolet™ iN™10 Infrared Microscope Thermo Scientific, it couples optic microscopy with IR spectroscopy. Two different detectors are present: DTG (Deuturate Triglycine sulfate) detector enables room temperature analysis, and MCT (Mercury Cadmium Telluride ) detector works with liquid nitrogen. Infrared resolution: 10 µm. However, it allows the analysis of samples down to 5 µm, thanks to the pretreatments developed. Samples can be analyzed in transmittance mode, reflectance mode, and ATR mode.
Nicolet RaptIR-FTIR Microscope: The Nicolet RaptIR is adapted to interface with a Nicolet iS50 FTIR Spectrometer It is equipped with a MCT (Mercury Cadmium Telluride ) detector, using liquid nitrogen. Samples can be analyzed in transmittance, reflectance, and ATR modes. It is also equipped with a NIR detector. Visible resolution down to 1 µm, Infrared resolution down to 5 µm.Research areas and applications
Particles Analysis via Nicolet™ iN™10 and via Nicolet RaptIR-FTIR Microscope can be performed on filters, where microplastics and other anthropogenic litter were collected after the extraction from several environmental matrices: seawater, wasterwater, stormwater, drinking water, wet and dry depositions, atmospheric aerosol, snow, sediments, soil, permafrost, organisms, e.g., mussels, clams, small benthic and zooplanktonic invertebrates, crustaceans, fish. The analysis can also be performed on large microplastics (from 5 mm down to 1 mm). Particles analysis via Micro-FTIR allows quantification and simultaneous polymer identification of plastic particles (including bioplastics), and of other anthropogenic particles such as plastic additives, (e.g., cross-linkers, vulcanizers, antioxidants, lubricants, flame retardants, plasticizers, etc), artificial and natural fibers. It can be employed for analysis of microplastics, but also for analysis of microfossils, artistic handiworks, pharmaceutical, etc. The instruments are equipped with various reference libraries.
Science highlights
Corami, F., Rosso, B., Morabito, E., Rensi, V., Gambaro, A., & Barbante, C. (2021). Small microplastics (< 100 μm), plasticizers and additives in seawater and sediments: Oleo-extraction, purification, quantification, and polymer characterization using Micro-FTIR. Science of the Total Environment, 797, 148937.
Corami, F., Rosso, B., Bravo, B. (2025). Improved Analysis of Microplastics and Other Microlitter Components in Environmental Samples. Application note. Thermofisher Scientific. Wisconsin, US. https://documents.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/CAD/Application-Notes/microplastics-and-microlitter-analysis-mcs-an1267-en.pdf
Rosso, B., Gregoris, E., Litti, L., Zorzi, F., Fiorini, M., Bravo, B., … & Corami, F. (2023). Identification and quantification of tire wear particles by employing different cross-validation techniques: FTIR-ATR Micro-FTIR, Pyr-GC/MS, and SEM. Environmental Pollution, 326, 121511.


