Micrometrics 3FLEX
General Information
Unit
CNR IPCBTechnique
Key Instrumentation
Physisorption & ChemisorptionHigh-performance gas adsorption analyzer for measuring surface area, pore size, and pore volume of powders and particulate materials, microporous and mesoporous materials.
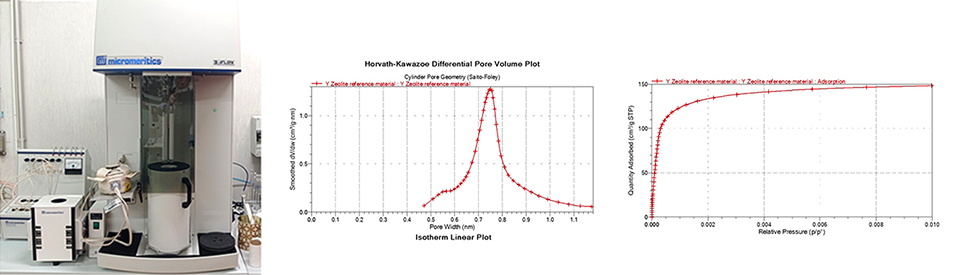
Technical description
IN13 is a backscattering spectrometer working with thermal neutrons with wavelength 2.23 Ǻ corresponding to energy of 16.45 meV. The variation of the incident neutron energy is obtained by adjusting the d-spacing of the monochromator by heating/cooling it. The energy resolution is of the order of 8 μeV and the energy window is ± 150 μeV, corresponding to a time scale ranging from 10- 12 s to 10-10 s. The neutrons leaving the guides are selected in energy by a CaF2 monochromator and then reflected by a pyrolytic graphite deflector to finally reach the sample through a chopper device. The beam dimension at the sample position is defined by a double-slit system. The beam scattered from the sample is reflected in almost perfect backscattering geometry by CaF2 analysers mounted on spherically/circularly curved Al plates, to be finally collected by 35 He3 gas counter detectors and a position-sensitive detector for the medium-large and small scattering angles, respectively. The background noise is minimized through the insertion of a conic collimator covered with gadolinium paint. The instrument fills the energy gap between IN10 or IN16 and IN5 at ILL, MIBEMOL at the LLB or IRIS at the Rutherford-Appleton laboratory (RAL) in United-Kingdom. In addition the value of the incident energy gives the availability of high momentum transfers (Q < 4.9 Å-1, extendable to 5.5 Å-1), much larger than obtainable with the above-mentioned spectrometers.
Research areas and applications
Applications are found in biology, medical science, chemistry, cultural heritage, etc. Among them:
- Physics: order-disorder phase transition in imogolite nanotubes, energy storage, etc
- Biology: cellular response to external signals and extreme conditions (high P, high T, pH, etc.), studies of whole cells in vivo, etc.
- Agricultural science: mechanisms of seed germination to perpetuate plants.
- Biomedicine: properties of water diffusion in cerebral tissues with important implications for a deeper understanding of cerebral pathologies.
- Chemistry: biopolymer hydrogels and their pharmaceutical and medical applications.
Science highlights
